Brain- Molecular Hydrogen as a Neuroprotective Agent
Conclusion
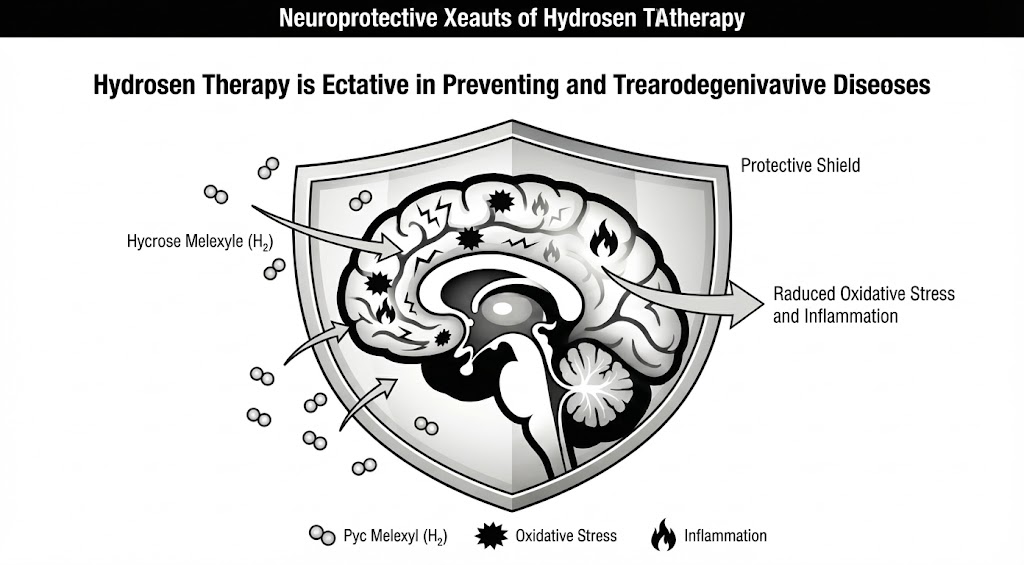
- The study examined the neuroprotective effects of hydrogen (H₂) therapy in animal models and human clinical studies experiencing neurodegenerative damage induced by oxidative stress.
- Hydrogen was administered through three routes: H₂ gas inhalation, ingestion of H₂-dissolved water, and injection of H₂-dissolved saline, exerting its effects primarily by selectively reducing highly toxic reactive oxygen radicals (·OH) and peroxynitrite.
- Hydrogen therapy significantly reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury (IRI) and other neurodegenerative disorders, demonstrating neuroprotective effects (p < 0.05) and being proposed as a clinically safe and effective therapeutic alternative.
Photobiomodulation Treatment Device
Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber
Hydrogen Inhalation Machine
Nano-bubble Hydrogen
Water Generator
Whole Body Wave
Motion Exercise Device
Nitro Biome
BAHI Longevity
Product Background
References
Customer Center
Get In Touch
- Haan-ro, Gwangmyeong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea
- +82)2-898-2116
- info@huelight.kr
Copyright 2026 © Hue Light Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: The medical papers and academic information provided on this site are intended for educational purposes only and are not meant to
diagnose, treat, prevent diseases, or substitute for a doctor’s advice.
